Earth Day 2022: Thinking globally still matters!
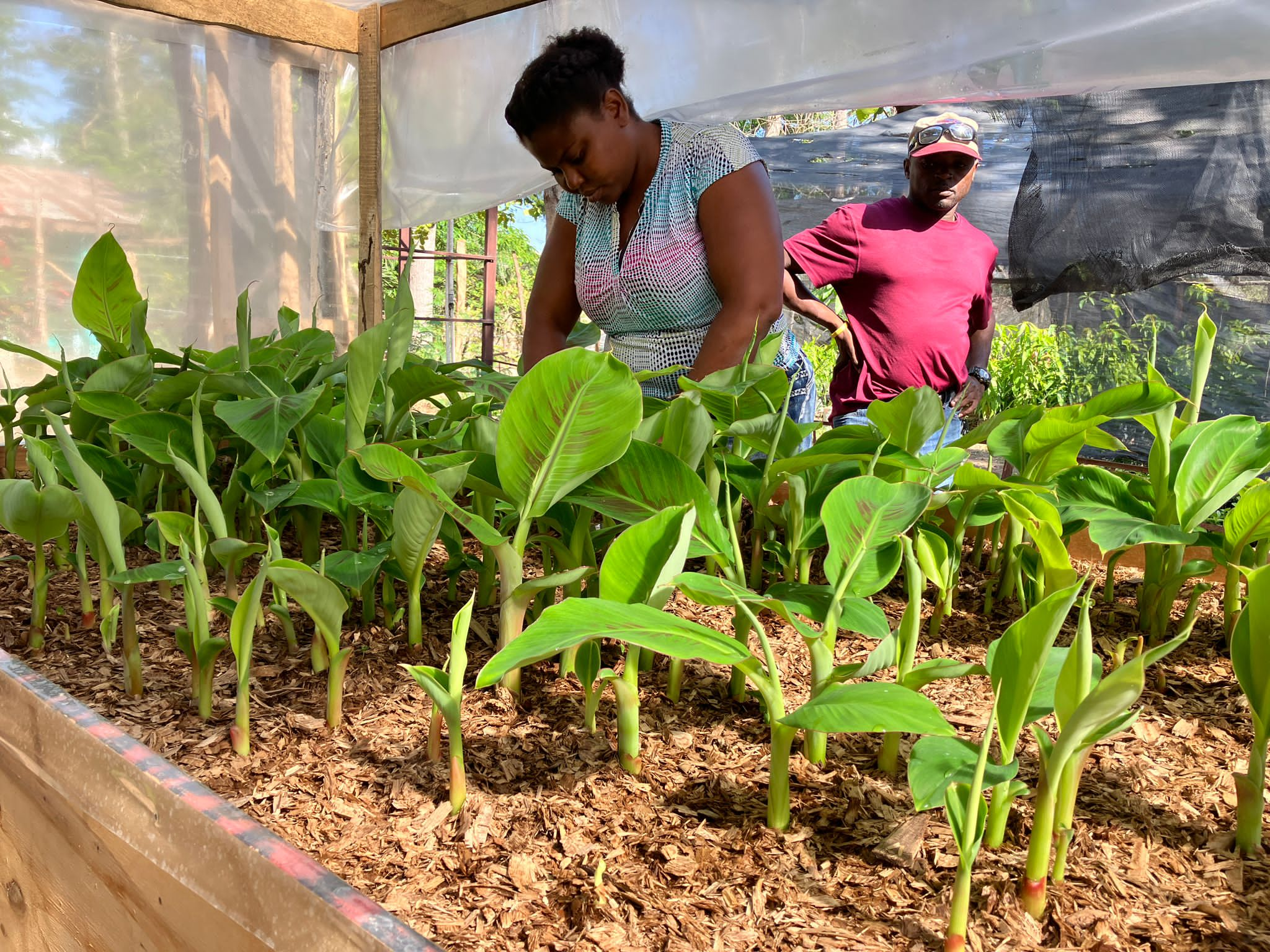
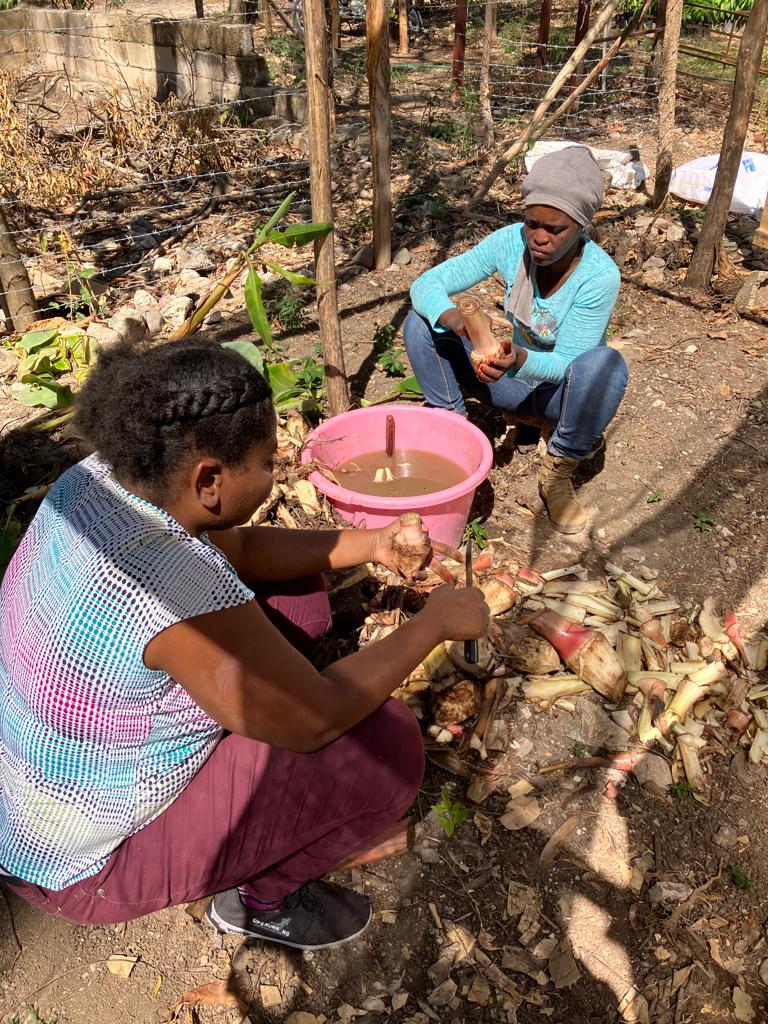
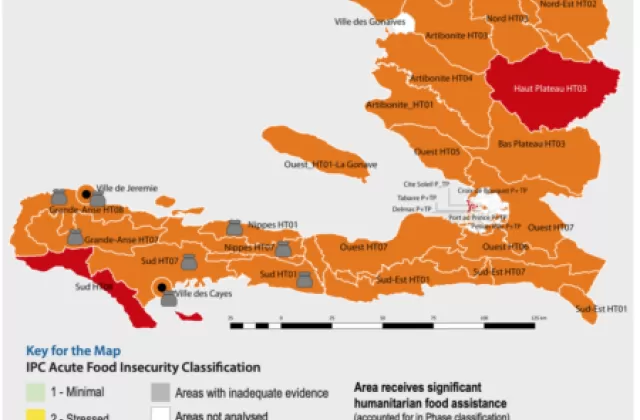
In Haiti 4.5 million people are experiencing high levels of food insecurity today, with roughly 45% of the population expected to face severe hunger over the next several months; 1.3. million of them are in an emergency situation. Based on IPC classifications of food insecurity, all of Haiti's regions are at level 3 or 4, meaning that in every department, there is hunger. Level 3 means there is either not enough food, or people can only eat enough if they forego other necessities.